-
-
FeaturesคุณสมบัติPenyelesaianRecursosFiturCaracterísticas精选功能精選功能المزايا
-
Solutionsโซลูชั่นPenyelesaianSoluçõesSolusiSoluciones解决方案解決方案الحلول
-
IntegrationsการผสานรวมIntegrasiIntegraçõesIntegrationsIntegraciones集成平台整合دمج مع تطبيقات أخرى
-
Affiliate/Partnersพันธมิตร/พันธมิตรทรัพยากรAfiliasi/Rakan KongsiAfiliados/ParceirosAfiliasi/MitraAfiliados/Partners联盟/合作伙伴聯盟/夥伴شريك
-
ResourcesจองการสาธิตSumberRecursosSumber dayaRecursosالموارد
Understanding WhatsApp Data Security: End-to-End Encryption and Backups
In today’s digital world, privacy and security are vital. This blog explores WhatsApp’s data security, covering end-to-end encryption and backups. Learn how WhatsApp protects your data and how to stay secure in the digital landscape.
What is WhatsApp Data Security
WhatsApp’s data security is super important because it has over two billion users worldwide. It’s a big player in personal and professional messaging. But because it’s so popular, it’s also a target for security threats. That’s why it uses robust security measures.
At its core, WhatsApp data security is all about keeping your chats and personal stuff private and secure. WhatsApp uses special security features to do this. Two big ones are end-to-end encryption and backups.
So, WhatsApp takes your data security seriously to protect your messages and info.
Also read: WhatsApp Privacy and Security: Tips to Keep Your Chats Safe
Explanation of End-to-End Encryption
WhatsApp utilizes end-to-end encryption to secure your messages. This encryption method ensures your conversations remain private and secure, even if they pass through WhatsApp’s servers. It means that when you send a message, it’s encrypted on your device and can only be decrypted by the recipient’s device, with no intermediary, including WhatsApp, having access to your message’s content.
How End-to-End Encryption Works in WhatsApp
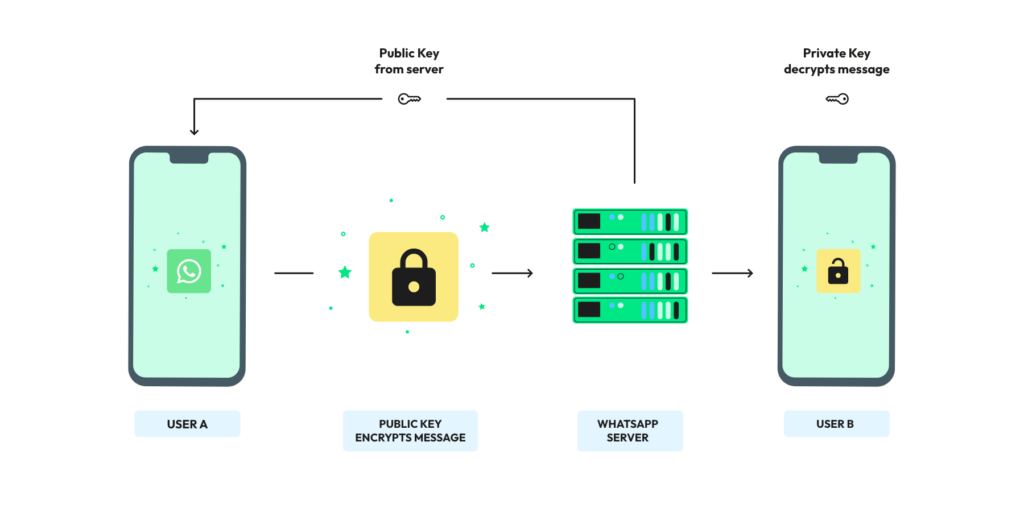
It works by encrypting the contents of your messages on your device, and only the recipient’s device can decrypt and read the messages. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how end-to-end encryption works in WhatsApp:
1. Key Generation
When you first install WhatsApp, the app generates a pair of cryptographic keys—a public key and a private key—for your device. The public key is shared with other users, while the private key is stored securely on your device and never leaves it.
2. Key Exchange
When you start a conversation with someone on WhatsApp, the app automatically exchanges public keys between your and recipient’s devices. This exchange of keys happens silently in the background, and you don’t need to manage encryption keys manually.
3. Message Encryption
When you send a message to a contact, WhatsApp encrypts the message on your device using the recipient’s public key. This encryption process transforms your message into unreadable gibberish or ciphertext and then sends it to WhatsApp’s servers.
4. Server Relay
WhatsApp’s servers act as relays for encrypted messages. They receive the ciphertext and forward it to the recipient’s device.
5. Message Decryption
Upon receiving the ciphertext, the recipient’s device uses their private key to decrypt the message. This private key is securely stored on their device and is the only key capable of deciphering the ciphertext.

6. Message Display
Once the recipient’s device decrypts the ciphertext, it displays the message in its original, readable form.
7. End-to-end Encryption in Group Chats: WhatsApp also employs end-to-end encryption. Each group has its encryption key, and messages are encrypted and decrypted individually for each group member. This approach ensures that only group members can read the messages sent within their group.
Key points to note about WhatsApp’s end-to-end encryption:
- WhatsApp cannot read your messages’ content because it cannot access your private keys.
- Your messages are only accessible to you and the recipient(s) you’re communicating with.
- End-to-end encryption covers text messages, voice calls, video calls, and multimedia files shared within chats.
Benefits and Importance of End-to-End Encryption for User Privacy
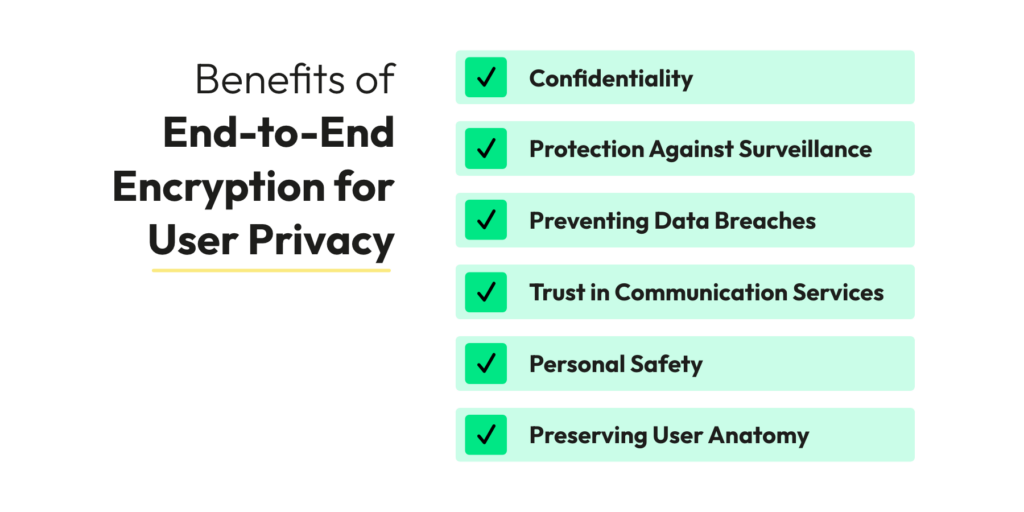
1. Confidentiality
With end-to-end encryption (E2E), you get the assurance that only you and the person you’re chatting with can read what’s in your messages. This powerful feature means that even service providers or intermediaries like messaging apps or email services can’t peek into your data. This confidentiality is crucial for keeping your private chats and personal info safe and secure.
2. Protection Against Surveillance
E2E encryption is a potent defense against unauthorized surveillance by governments, hackers, or malicious entities. It prevents the bulk collection of data by ensuring that communication remains private and inaccessible to third parties.
3. Preventing Data Breaches
End-to-end encryption (E2E) minimizes the risk of data breaches. Even if a service provider’s servers are compromised, the encrypted data stored on those servers remains unreadable without the private keys held by the users. This security measure significantly reduces the likelihood of sensitive information falling into the wrong hands.
4. Trust in Communication Services
Knowing that their communications are end-to-end encrypted instils trust in users. It reassures them that their personal messages, photos, videos, and sensitive documents are protected, fostering a sense of security and confidence in using digital communication platforms.
5. Protecting Business and Professional Communication
For businesses and professionals, E2E encryption is essential for safeguarding confidential client information, proprietary data, and trade secrets. It ensures that sensitive business discussions and transactions remain private and secure.
6. Personal Safety
End-to-end encryption (E2E) is vital for individuals facing personal safety risks when disclosing sensitive information. This category includes whistleblowers, activists, journalists, and individuals in oppressive regimes. Encrypted communication is a lifeline for those sharing crucial information while safeguarding their identity.
7. Preserving User Autonomy
E2E encryption empowers users to control their data and who has access to it. It prevents service providers from monetizing user data without consent and helps users maintain digital autonomy.
8. Legal and Ethical Compliance
Many countries and industries have regulations requiring user data protection and privacy. Implementing E2E encryption can help organisations comply with these legal requirements and maintain their ethical responsibilities toward their users.
9. Mitigating Insider Threats
E2E encryption can also guard against insider threats within organisations. Employees with access to systems and data cannot read encrypted messages without decryption keys.
10. Global Standard for Privacy
E2E encryption has become a global standard for ensuring digital privacy. It has raised the bar for security across various communication platforms, encouraging the adopting of more robust encryption practices.
Key Features of WhatsApp’s End-to-End Encryption
Message Encryption and Decryption Process
Message encryption and decryption are like secret codes safeguarding your important communication information. First, your message transforms into a code (encryption), which someone can reverse to retrieve your original message (decryption). Let’s examine in detail how this process operates:
Message Encryption:
1. Data Preparation: The process begins with the sender preparing the message they want to send. This message can be plain text, files, images, or any other data type.
2. Encryption Algorithm: An encryption algorithm is applied to secure your message. This algorithm uses a specific encryption key, a symmetric key (the same key used for encryption and decryption) or an asymmetric key pair (a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption).
3. Encryption Process: The encryption algorithm processes the message and the encryption key to transform the original message into ciphertext. Ciphertext is a scrambled version of the message that appears as random characters or data and is unreadable without the decryption key.
4. Transmission: The sender transmits the ciphertext to the recipient, typically through a communication channel such as the internet, email, or a messaging app.
Message Decryption:
5. Ciphertext Reception: The recipient receives the ciphertext sent by the sender.
Decryption Key: The recipient needs the appropriate key to decrypt the message. In symmetric encryption, this is the same key used for encryption. In asymmetric encryption, the recipient uses their private key, corresponding to the sender’s public key used for encryption.
6. Decryption Process: Using the decryption key, the recipient’s device applies the decryption algorithm to the received ciphertext. This process reverses the encryption and transforms the ciphertext into the original plaintext message.
7. Message Presentation: Once the decryption process is complete, the recipient can access and read the original message, which is in its readable form.
It’s important to note that this process’s security depends on the encryption algorithm’s strength and the encryption keys’ secrecy. Strong encryption algorithms are designed to withstand attacks that reverse encryption without the correct key. Furthermore, you must keep the keys secure and share them only with trusted parties to prevent unauthorized decryption.
Message encryption and decryption are crucial in digital communication. This security process helps protect messages, emails, online banking transactions, and sensitive information when transmitted over the Internet. These steps are essential for safeguarding your data, preserving business secrets, and maintaining privacy in today’s interconnected world.
Security of Voice and Video Calls on WhatsApp
WhatsApp takes the security of voice and video calls seriously, employing end-to-end encryption to protect the content of your calls. Here’s how WhatsApp ensures the security of your voice and video calls:
End-to-end Encryption
WhatsApp uses the same robust end-to-end encryption for voice and video calls as text messages. Your device encrypts your calls, and only the recipient’s device can decrypt and play the audio or video stream. No one, not even WhatsApp, can intercept or listen to your calls.
Encryption Keys
In a call, every participant creates encryption keys just for that session. These keys are temporary and unique to that call; they don’t save or reuse them later. This extra security layer ensures that if someone compromises the keys, it won’t affect any other calls, past or future.
Secure Signal Protocol
WhatsApp employs the Signal Protocol for end-to-end encryption, a highly regarded protocol known for its security features. It guarantees the confidentiality and integrity of your voice and video calls.
Verification
WhatsApp allows users to verify the security of their calls by comparing security codes with their contacts. This helps ensure that no one is intercepting or impersonating the call.
Secure Server Relay
While WhatsApp’s servers facilitate call setup and relay the encrypted data between devices, they do not have access to the actual content of your calls due to end-to-end encryption. This means that even if someone gains access to WhatsApp’s servers, they cannot eavesdrop on your conversations.
Group Calls
WhatsApp extends end-to-end encryption to group voice and video calls. This ensures that group communications remain private and secure, with each participant’s communication encrypted individually.
No Call Logs
WhatsApp does not keep logs of your calls, which further enhances your privacy. The absence of call records on WhatsApp’s servers means no centralized repository of your call history.
While WhatsApp’s end-to-end encryption provides vital protection for your voice and video calls, it’s essential to remember that the security of your calls also depends on the safety of the devices you use. Keeping your device’s operating system and WhatsApp app up to date, using a secure and unique device PIN or passcode, and avoiding potentially compromised networks or devices are additional steps to enhance the security of your voice and video calls.

Verification Methods for Ensuring Secure Communication
Ensuring secure communication is essential, especially in an age where privacy concerns and data breaches are prevalent. Verification methods are crucial in confirming the authenticity of communication partners and the data’s integrity. Here are some standard verification methods for ensuring secure communication:
End-to-end Encryption
Utilizing end-to-end encryption is one of the most effective ways to secure communication. It ensures that data is encrypted on the sender’s device and only decrypted on the recipient’s device. Verification occurs through cryptographic keys, and users can confirm the security of their communication by comparing security codes or scanning QR codes.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two different authentication factors. Typically, this involves something they know (e.g., a password) and something they have (e.g., a one-time code from a mobile app or hardware token). By requiring both factors, 2FA helps verify the user’s identity.
Biometric Verification
Biometrics, such as fingerprint scans or facial recognition, can verify a user’s identity. These methods are difficult to fake and provide high confidence in the user’s authenticity.
Secure Tokens and Hardware Keys
Hardware security keys or tokens generate one-time codes that users must provide to access an account or complete a transaction. These physical devices add a strong layer of verification as they are not susceptible to remote attacks.
Certificate Authorities (CAs)
In the context of secure websites (HTTPS), CAs issue digital certificates that verify the authenticity of a website’s identity. Browsers can confirm the certificate’s legitimacy, providing a secure connection to the website.
Visual Verification
Visual verification may sometimes be used, especially with in-person communication or exchanges of sensitive information. This can include checking government-issued IDs, comparing photos, or using QR codes for confirmation.
Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technologies
Blockchain and distributed ledgers can provide secure and tamper-proof verification. Smart contracts and public logs can confirm the authenticity and integrity of transactions and data.
Voice or Video Verification
For specific applications, voice or video verification can be used to confirm a person’s or party’s identity during communication. Voiceprints and facial recognition can be employed for this purpose.
Timestamps
Timestamps record when a communication or document was created or modified. They can be used to ensure the document’s integrity and to establish a clear timeline.
The choice of verification method depends on the specific context and level of security required. In many cases, a combination of these methods can be employed to create a robust security framework for communication, ensuring that data remains confidential, messages are not tampered with, and the parties’ identity is verified.
Limitations and Considerations of End-to-End Encryption
End-to-end encryption (E2E) is a powerful tool for ensuring the privacy and security of digital communication. Still, it also has limitations and considerations that users, organizations, and policymakers should know. Here are some fundamental limitations and considerations of E2E encryption:
1. Key Management
- Key Distribution: Securely exchanging encryption keys between users can be challenging. If keys are not handled properly, they can be a weak link in the security chain.
- Key Loss: If users lose their encryption key or password, they may permanently lose access to their encrypted data.
2. No Central Recovery
E2E encryption systems are designed so service providers cannot recover users’ data. While this is great for privacy, it can also mean that data recovery may be impossible if users forget their passwords or lose their keys.
3. Limited Metadata Protection
While E2E encryption protects the content of messages, it does not necessarily protect metadata, such as who is communicating with whom, when, and for how long. Metadata can reveal patterns of communication and is not always encrypted.
4. User Errors
E2E encryption relies on users to verify the identity of their communication partners and confirm encryption keys. Users may mistakenly verify the wrong keys or ignore security warnings.
5. Incompatibility
E2E encryption may not be compatible with all communication platforms or devices. This can limit the ability to have encrypted conversations with everyone, as both parties must use compatible software.
6. Backups
Backing up E2E-encrypted data can be challenging. If you lose your device or backup, you may be unable to recover your messages.
7. Legal and Regulatory Challenges
Some governments and regulatory bodies have expressed concerns about E2E encryption, as it can impede law enforcement’s ability to access communications for legitimate purposes, such as criminal investigations.
8. Misuse and Abuse
Malicious people can use E2E encryption to hide illicit activities, such as cybercrime or terrorist communication. This raises ethical and legal concerns and has prompted debates about balancing privacy and security.
9. Updates and Vulnerabilities
E2E encryption systems require regular updates and maintenance to patch security vulnerabilities. Failure to keep software up to date can lead to security breaches.
10. Impact on Services
E2E encryption can introduce latency and resource demands on services, potentially affecting the user experience, especially in real-time applications like video calls.
11. Trust in Third Parties
Users must trust the developers of E2E encryption software to implement the encryption correctly and not introduce backdoors or vulnerabilities. The trustworthiness of third-party software is paramount.
Managing and Securing WhatsApp Backups

Managing and securing WhatsApp backups is crucial for preserving your chat history while maintaining the privacy and security of your data. WhatsApp provides options for backing up your chats to cloud services like Google Drive (on Android) or iCloud (on iOS) and offers end-to-end encryption for these backups. Here’s how to manage and secure your WhatsApp backups effectively:
1. Regular Backup Schedule
Enable automatic backups in WhatsApp to ensure that your chat history is regularly saved. You can choose how often the backups occur (daily, weekly, or monthly).
2. Enable End-to-End Encryption
WhatsApp now offers end-to-end backup encryption, ensuring that even the cloud storage provider cannot access your chat history. To enable this:
- On Android: Go to WhatsApp > Settings > Chats > Chat backup > toggle on “End-to-end encryption.”
- On iOS: WhatsApp backups to iCloud are already end-to-end encrypted by default.
3. Use Strong Authentication
Secure your cloud storage account (Google Drive or iCloud) with robust authentication methods, such as two-factor authentication (2FA). This provides an additional layer of security for your backups.
4. Choose a Strong Password
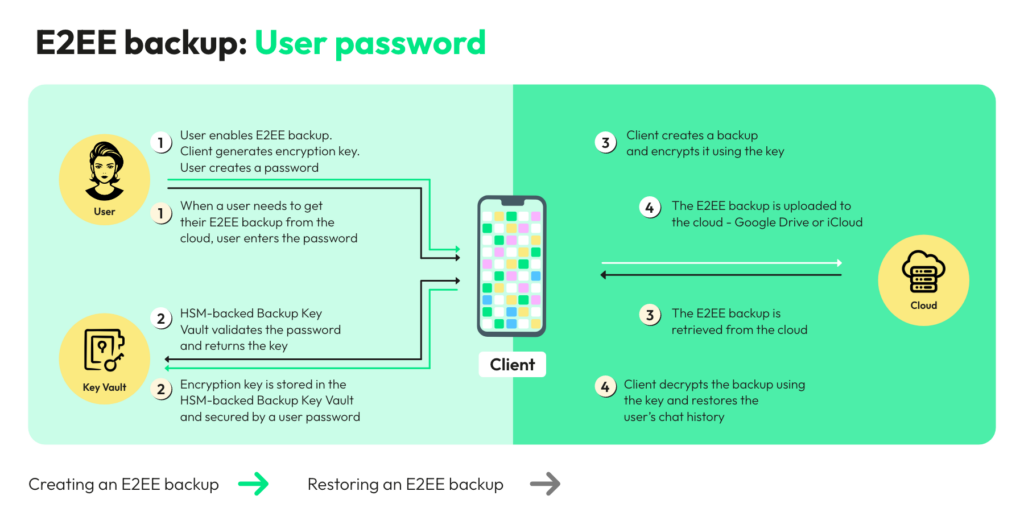
When prompted to set up a backup password (for Android users who enable end-to-end encryption), choose a strong and unique password. Store this password securely, as it will be required for restoring your backups.
5. Check Backup Settings
Review your backup settings regularly to ensure they match your preferences. Confirm the backup frequency, which Google Drive or iCloud account you use, and the option to include videos.
6. Manage Backup Storage
Keep an eye on your cloud storage space, as WhatsApp backups can consume significant storage over time. Delete old or unnecessary backups to free up space.
7. Secure Your Mobile Device
Protect your smartphone or tablet with a strong lock screen PIN, password, or biometric authentication to prevent unauthorized access to your WhatsApp account and backups.
8. Safeguard Backup Password
If you use a backup password for Android end-to-end encryption, store it securely. Losing this password may prevent you from restoring your backups.
9. Verify Encryption Keys
When you restore a backup, verify the encryption keys with WhatsApp to ensure that your data hasn’t been tampered with or compromised during the restoration process.
10. Be Cautious with Third-Party Backup Services
Avoid using third-party backup services or apps that claim to back up WhatsApp data. Stick to the official backup options provided by WhatsApp to ensure security.
11. Consider Local Backups:
WhatsApp allows you to create local backups on your device’s internal storage. These are not stored in the cloud and are usually easier to manage and secure.
By following these steps, you can effectively manage and secure your WhatsApp backups, ensuring the privacy and integrity of your chat history while keeping it accessible for future use or device transfers.
Also, check our Google Chrome extension, which can help you with WhatsApp chat backups.
Best practices for securing WhatsApp backups
Securing WhatsApp backups is essential for safeguarding your chat history and personal data. WhatsApp provides options for backing up your chats to cloud services like Google Drive (on Android) or iCloud (on iOS). Here are some best practices to help you secure WhatsApp backups effectively:

Use Strong Authentication for Cloud Storage:
Secure your Google Drive or iCloud account with robust authentication methods, such as two-factor authentication (2FA) or biometric authentication (e.g., Face ID or Touch ID). This adds an extra layer of security to your cloud storage.
Choose a Strong Backup Password
Set a strong and unique backup password if you’re using Android and enabling end-to-end backup encryption. This password is required for restoring your backups, so store it securely.
Safeguard Backup Password
If you set a backup password for Android end-to-end encryption, store it securely. Losing this password may result in the inability to restore your backups.
Educate Yourself About Backup Security
Stay informed about WhatsApp’s backup security features and practices by regularly checking the official documentation and news updates from WhatsApp.
Protecting User Data on WhatsApp
Importance of Device Security and Passcode Protection
Device security and passcode protection are paramount in today’s digital age, where smartphones, tablets, and computers have become integral parts of our personal and professional lives. These security measures safeguard sensitive information, personal data, and digital privacy. Here’s why device security and passcode protection are so vital:
Prevention of Unauthorized Access
Passcodes, PINs, passwords, or biometric authentication methods (e.g., fingerprint or facial recognition) serve as barriers to prevent unauthorized individuals from accessing your device. This helps protect your personal data, accounts, and online activities from prying eyes.
Protection of Personal Information
Modern devices store a wealth of personal information, including contacts, messages, emails, photos, documents, and more. Proper security measures ensure that this information remains confidential and cannot be easily accessed by unauthorized users.
Preventing Identity Theft
Your device often contains access to your email, social media accounts, banking apps, and more. Unauthorized access to these accounts can lead to identity theft, financial fraud, or other cybercrimes. Strong device security is a critical defense against these threats.
Securing Payment and Financial Apps
Many people use mobile banking and payment apps, which store sensitive financial data. A secure device prevents unauthorized transactions and protects your financial assets.
Data Privacy and Compliance
Ensuring the security of your device is essential for maintaining data privacy and compliance with various data protection regulations, such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) or HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act).
Protection Against Physical Theft
If your device is stolen or lost, a passcode or biometric lock helps prevent the thief from accessing your data. Remote wiping features can also be activated to remotely erase data from the device.
Preventing Unauthorized App Access
Passcode protection can extend to individual apps, adding an extra layer of security for sensitive apps like email, messaging, or note-taking apps.
Protecting Personal Communication
Device security ensures the privacy of your calls, text messages, and online chats. Unauthorized access to these communications can have profound implications.
Safeguarding Business Data
For professionals and businesses, device security is critical for protecting sensitive work-related data, emails, and proprietary information. A compromised device can lead to data breaches and intellectual property theft.
Maintaining Online Account Security
Your device is often used to access various online accounts, including email, social media, and cloud storage. A compromised device can provide attackers with a gateway to your online accounts.
Family and Child Safety
Device security is essential for parents to control and monitor their children’s access to content and apps, protecting them from inappropriate material or online threats.
Overall Digital Hygiene
Good device security practices are fundamental to digital hygiene. They reduce the risk of malware infections, phishing attacks, and other cyber threats.
Two-Step Verification and Additional Security Features
Two-step verification (2SV), or two-factor authentication (2FA), is a vital security feature that protects your online accounts, including email, social media, banking, and more. In addition to two-step verification, several other security features and practices can further enhance your account security. Here’s a look at two-step verification and some additional security features:
Two-Step Verification (2SV/2FA):
Two-step verification is a security process that requires users to provide two different authentication factors before gaining access to their accounts. These factors typically fall into three categories:
- Something You Know: This is typically a password or PIN only you should know.
- Something You Have: This involves possessing a physical device or a one-time code generated by an authentication app or sent to you via text or email.
- Something You Are: This factor relates to biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or facial recognition.
Here’s how two-step verification works:
- After entering your username and password (something you know), you’ll be prompted to provide a second factor (something you have or are) to complete the authentication process.
- Common second factors include a one-time code sent to your mobile device, generated by an authentication app (like Google Authenticator or Authy), or a fingerprint or facial scan.
- Even if someone has your password, they cannot access your account without the second factor, significantly improving security.
Additional Security Features and Practices:
In addition to two-step verification, consider implementing the following security features and practices to protect your online accounts further:
Biometric Authentication: Use biometric authentication methods like fingerprint recognition or facial ID for added security wherever possible.
Password Manager: Use a reputable password manager to generate, store, and autofill complex and unique passwords for each account. This minimizes the risk of password reuse.
Account Recovery Options: Set up account recovery options such as secondary email addresses or phone numbers to regain access to your accounts if you forget your password or are locked out.
Security Questions: Avoid using easily guessable answers for security questions, and consider providing fictional solutions that only you would know.
Email Security: Secure your email account with a strong password and two-step verification, as email accounts are often used for password resets on other accounts.
Device Security: Secure your devices with strong passcodes, PINs, or biometrics to prevent unauthorized access.
App Permissions: Review and limit the permissions granted to apps on your devices to minimize potential vulnerabilities.
Regular Software Updates: Keep your operating system, apps, and security software updated to patch vulnerabilities.
Monitoring Your Accounts: Regularly review your account activity and set up notifications for unusual or suspicious activity.
Beware of Phishing: Be cautious about unsolicited emails, messages, or links, especially those requesting sensitive information. Verify the legitimacy of requests before responding.
Secure Networks: Use secure, trusted networks and avoid public Wi-Fi for sensitive transactions whenever possible.
Ensuring Privacy in Group Chats and Multimedia Sharing
For Group Chats:
Choose Secure Messaging Apps: Select messaging apps that offer end-to-end encryption for group chats. WhatsApp, Signal, and Telegram are apps prioritising security and privacy.
Verify Group Members: Before sharing sensitive information, verify the identity of group members. Confirm that everyone in the group is who they claim to be.
Use Strong Authentication: Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for your messaging app to prevent unauthorized access to your account.
Set Group Privacy Settings: Many messaging apps allow you to set group privacy settings. You can control who can join the group and who can add you to new groups. Choose the settings that align with your privacy preferences.
Avoid Public Groups: Be cautious when joining public groups, as they may expose your identity and discussions to a broader audience. Opt for private or invite-only groups whenever possible.
Limit Sharing of Personal Information: Avoid sharing personal information like phone numbers, addresses, or sensitive documents in group chats, especially if you are unfamiliar with all group members.
Use Disappearing Messages: Some messaging apps offer a feature where messages automatically disappear after a set period. Enable this feature for sensitive group conversations to reduce the indefinite storage risk.
For Multimedia Sharing:
Check Metadata: Be aware that photos and videos often contain metadata (EXIF data) that may include details like the location where the media was captured. Before sharing, remove or scrub this metadata to protect your privacy.
Share Privately: If you need to share sensitive multimedia, send them privately to specific recipients instead of sharing them in group chats. Most messaging apps allow you to have private, one-on-one conversations.
Use Encryption for Cloud Storage: If you use cloud storage services to share multimedia (e.g., Google Drive, iCloud), enable end-to-end encryption for those services to protect your files.
Secure Photo and Video Apps: Use secure and private photo and video apps with encryption and additional privacy features. These apps can help you maintain control over your multimedia content.
Beware of Screenshots: Recipients can take screenshots of the multimedia you share, potentially sharing it with others without your knowledge. Be selective about what you share and with whom.
Consider Self-Destructing Media: Some apps and services offer self-destructing multimedia options, where the content disappears after a certain period. Use these features for added privacy.
Password-Protect Files: If you need to share sensitive multimedia files, consider password-protecting them before sharing. Share the password separately from the media.
Avoid Automatic Backups: Disable automatic backups of your multimedia to cloud services if you’re concerned about their privacy. Manually back up only the content you’re comfortable storing in the cloud.
Regularly Review Shared Content: Review the content you’ve shared in group chats or privately. Delete any media that is no longer needed to reduce the digital footprint.
WhatsApp’s Data Handling Policies and Transparency
Data Handling Policies:
End-to-end Encryption: WhatsApp is known for its strong commitment to end-to-end encryption, which ensures that messages, voice calls, and video calls are only accessible to the sender and recipient. WhatsApp and even Facebook (its parent company) cannot access the content of these communications.
Minimal Data Collection: WhatsApp has historically collected minimal user data compared to other social media platforms. The core data collected includes phone numbers, profile names, and contact lists. It does not share the content of messages or calls with third parties.
Metadata: While the content of messages remains encrypted, some metadata, such as message timestamps, recipient information, and call logs, may be collected to improve service quality and prevent abuse.
Location Data: WhatsApp allows users to share their location with contacts, but this is optional and requires user consent.
Payment Information: WhatsApp introduced a payment feature in some regions. When users engage in payment transactions, WhatsApp may collect payment-related data to facilitate these transactions.
Transparency and Communication:
Privacy Policy Updates: WhatsApp faced scrutiny over changes to its privacy policy in early 2021, which initially raised concerns about data sharing with Facebook. The company clarified that the changes primarily applied to interactions with business accounts and that personal chats remained end-to-end encrypted.
In-App Notices: WhatsApp has used in-app notices to inform users about privacy policy changes, emphasizing the importance of transparency and user consent.
User Control: WhatsApp gives users control over various privacy settings, including who can see their profile information, who can contact them, and who can add them to groups. These settings aim to give users more control over their data and interactions.
Data Sharing with Facebook: WhatsApp had previously allowed limited data sharing with Facebook for targeted advertising on the platform. However, this practice was paused in most regions to address concerns about user privacy.
Security Features: WhatsApp has continued to invest in security features, such as two-step verification and biometric authentication, to enhance user data protection.
Transparency Reports: WhatsApp has issued transparency reports that provide information about government requests for user data and content removal, demonstrating its commitment to transparency regarding interactions with law enforcement agencies.
Common Myths and Misconceptions
Addressing Misconceptions About WhatsApp Data Security
Addressing misconceptions about WhatsApp data security is essential to provide accurate information and alleviate user concerns. WhatsApp has faced scrutiny and questions about its data handling practices, especially regarding changes to its privacy policy. Here are some common misconceptions and clarifications:
Misconception 1: WhatsApp Reads Your Messages
WhatsApp employs end-to-end encryption, which means that only the sender and the recipient of a message can read its content. WhatsApp cannot access or read your messages, whether text, voice, or video.
Misconception 2: WhatsApp Shares All Your Data with Facebook
WhatsApp shares limited data with Facebook, primarily for business communication purposes and advertising on Facebook’s platform. However, as of my last update in September 2021, WhatsApp clarified that personal chats remain end-to-end encrypted and are not used for advertising targeting.
Misconception 3: WhatsApp Stores All Your Chats in the Cloud
WhatsApp allows you to back up your chats to cloud services like Google Drive or iCloud. However, these backups are end-to-end encrypted, meaning the content is still protected even in the cloud. WhatsApp cannot access your chat history stored in these backups.
Misconception 4: WhatsApp Listens to Your Calls
WhatsApp does not listen to your voice or video calls. Like messages, calls made through WhatsApp are end-to-end encrypted, ensuring privacy.
Misconception 5: WhatsApp Has Access to Your Contacts’ Data
WhatsApp collects minimal contact information to facilitate communication with your contacts. However, this data is not used for marketing purposes or shared with third parties for advertising.
Misconception 6: WhatsApp Has Access to Your Location at All Times
WhatsApp allows users to share their real-time location with contacts, but this feature requires user consent and can be turned off anytime. WhatsApp does not track your location without your permission.
Misconception 7: WhatsApp Reads Your Messages for Spam or Ads
WhatsApp employs message filtering techniques to detect and prevent spam, scams, and abuse. However, this is done without accessing the content of your messages. WhatsApp uses metadata and patterns to identify potentially harmful messages.
Misconception 8: WhatsApp Does Not Prioritize Privacy
Clarification: WhatsApp has made privacy a central focus, with features like end-to-end encryption, two-factor authentication, privacy settings, and regular updates to enhance security. The platform has also resisted attempts to weaken encryption.
Misconception 9: WhatsApp Data Is Not Secure
While no system is immune to security risks, WhatsApp employs robust encryption and security measures to protect user data. Security vulnerabilities are regularly addressed through updates.
Misconception 10: WhatsApp Stores Your Payments Data
WhatsApp’s payment feature is designed to facilitate secure transactions, but it does not store payment details permanently. It follows stringent payment security standards.
Potential Advancements in Encryption and Backup Technologies
Encryption and backup technologies are crucial in securing data and ensuring its availability when needed. As technology continues to evolve, several potential advancements in these areas are on the horizon:
1. Quantum-Resistant Encryption
The advent of quantum computing poses a threat to traditional encryption methods. Quantum-resistant encryption algorithms are being developed to safeguard data against quantum attacks, ensuring long-term security.
2. Homomorphic Encryption
Homomorphic encryption allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without decrypting it. This technology has the potential to revolutionise data processing, enabling secure analysis in cloud environments and preserving privacy.
3. Post-Quantum Cryptography
As quantum computing advances, post-quantum cryptography aims to provide secure encryption methods immune to quantum attacks. Research is ongoing to identify and standardize these new cryptographic techniques.
4. Zero-Knowledge Proofs
Zero-knowledge proofs, such as zk-SNARKs (Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Argument of Knowledge), enable parties to prove the validity of a statement without revealing any underlying data. This technology enhances privacy and security in various applications.
5. Multi-Party Computation
Multi-party computation (MPC) enables multiple parties to jointly compute a function over their inputs while keeping those inputs private. MPC has applications in secure data analysis and collaborative tasks.
6. Improved Key Management
Advances in key management techniques are simplifying the secure generation, distribution, and rotation of encryption keys, reducing the risk of key-related vulnerabilities.
7. Federated Learning and Encrypted AI
Federated learning techniques enable machine learning models to be trained across multiple devices without sharing raw data. Combining federated learning with encryption ensures privacy while leveraging collective data for AI model improvement.
8. Decentralized and Blockchain-Based Encryption
Blockchain technology can enhance encryption and data security by providing decentralized and tamper-proof ledgers for key management, access control, and auditing.
9. Immutable and Tamper-Proof Backups
Advancements in blockchain and distributed ledger technologies can enable immutable and tamper-proof backup solutions. Data backups stored on decentralized networks can provide high security and data integrity.
10. Encrypted Cloud Storage with Zero-Knowledge Authentication
Enhanced cloud storage solutions are emerging, where users authenticate themselves with zero-knowledge proofs, ensuring that even the service provider cannot access the stored data.
11. Edge Computing and Secure Backups
Edge computing allows data processing to occur closer to the data source. This can lead to more secure backup solutions, with data processed and encrypted at the edge before being sent to centralized backups.
12. Privacy-Preserving Technologies for Backups
Privacy-preserving backup solutions are being developed to allow secure data backups while minimizing the exposure of sensitive information to backup providers.
13. Blockchain-Based Data Provenance:
Organizations can use blockchain technology to establish the provenance and authenticity of data backups, ensuring data integrity and reducing the risk of data tampering.
These potential encryption and backup technologies advancements aim to address emerging security challenges and enhance data protection and availability in an increasingly digital and interconnected world. As technology evolves, it’s crucial to stay informed about these developments to make informed data security and privacy decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is WhatsApp’s end-to-end encryption?
WhatsApp’s end-to-end encryption is a security feature that keeps your messages and calls private by ensuring only you and the recipient can read or hear them. It prevents anyone, including WhatsApp itself, from accessing the content without the encryption keys.
How does end-to-end encryption in WhatsApp ensure data security?
End-to-end encryption in WhatsApp keeps your data secure by encrypting messages on your device and only allowing the recipient’s device to decrypt and read them. This means WhatsApp and others can’t access your messages during transmission.
Can anyone other than the sender and recipient access WhatsApp messages?
Only the sender and recipient can access WhatsApp messages due to the platform’s end-to-end encryption. Messages are encrypted on the sender’s device and can only be decrypted on the recipient’s device, ensuring privacy and preventing access by anyone else, including WhatsApp.
What are the benefits of end-to-end encryption in WhatsApp for data security?
End-to-end encryption in WhatsApp ensures data security by keeping messages private, preventing unauthorized access, and boosting user trust.
How are WhatsApp backups secured?
Encryption and user authentication secure WhatsApp backups. Encryption ensures only the user can access the backup, and authentication verifies the user’s identity.
Are WhatsApp backups stored securely?
Yes, WhatsApp backups are stored securely. They are encrypted and can only be accessed by the authorized user through user authentication, enhancing the security of stored data.
Can WhatsApp decrypt and access backup data?
No, WhatsApp cannot decrypt or access backup data. Backups are encrypted with a unique key known only to the user, ensuring that WhatsApp cannot access the content. Only the user can decrypt and access their backup data.
Can end-to-end encryption and backups protect against device loss or theft?
You’re correct. WhatsApp cannot decrypt or access backup data. The user encrypts backups with a unique key known only to them, ensuring that WhatsApp cannot access the content. Only the user can decrypt and access their backup data. Thank you for clarifying this important point.
Are there any limitations or vulnerabilities to WhatsApp’s data security measures?
Yes, there are limitations and potential vulnerabilities in WhatsApp’s data security. These include the protection of backups, the user’s device, susceptibility to phishing, and compliance with government requests. User caution is essential.
Is WhatsApp compliant with data protection regulations?
WhatsApp has complied with data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and other relevant privacy laws. However, compliance can vary by region, and WhatsApp’s practices may evolve. We encourage users to review WhatsApp’s privacy policy and settings to understand how their data gets managed in their particular jurisdiction.
Latest Comments